Station Instructions: Assess this middle‑aged patient presenting with weight loss, tremor, heat intolerance or palpitations.1. Key History‑Taking Points
Clinical History
Symptoms of hyperthyroidism: weight loss despite appetite, sweating, heat intolerance, tremor, palpitations, dyspnoea, insomnia, anxiety, diarrhea, menstrual irregularities or hair loss
Neck symptoms: neck swelling, difficulty in breathing, difficulty in swallowing, voice changes, sleep apnoea
Duration & severity: progression timeline, impact on daily function
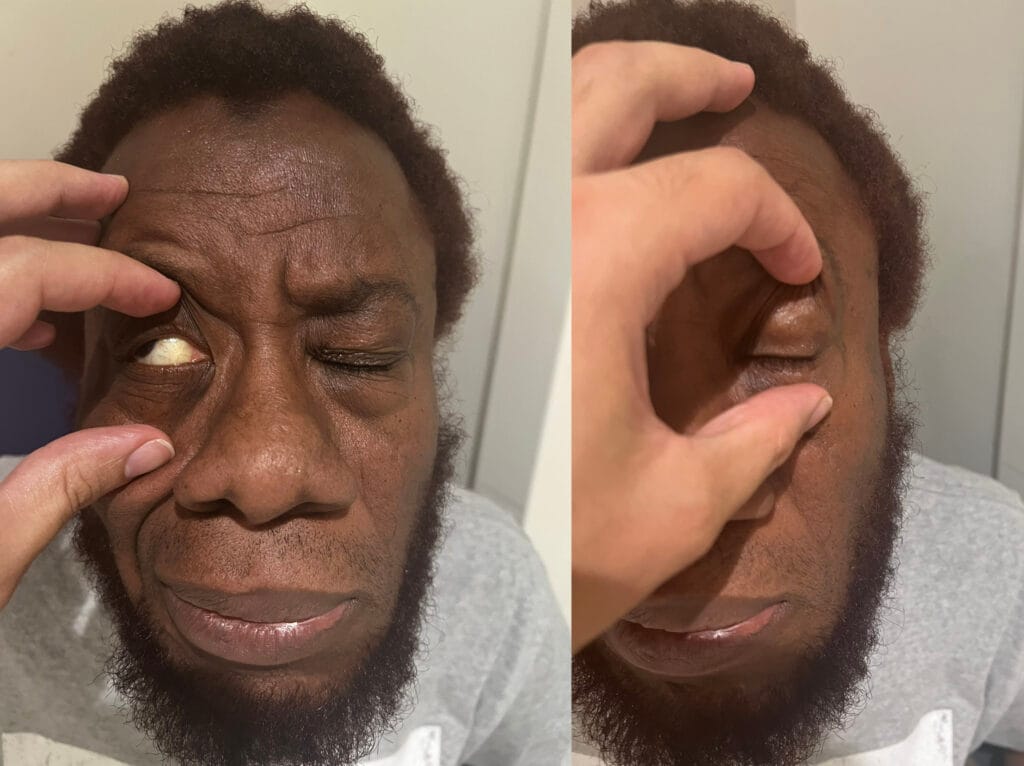
Eye symptoms: redness, swelling, photophobia, gritty sensation, diplopia, exophthalmos, eyelid retraction
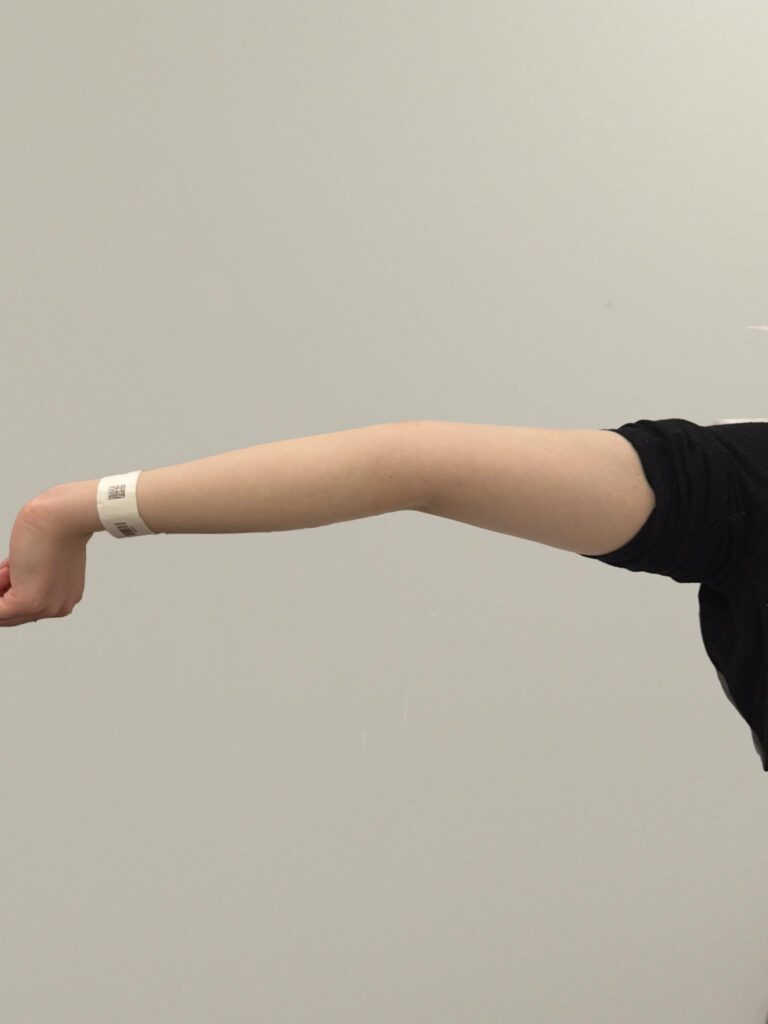
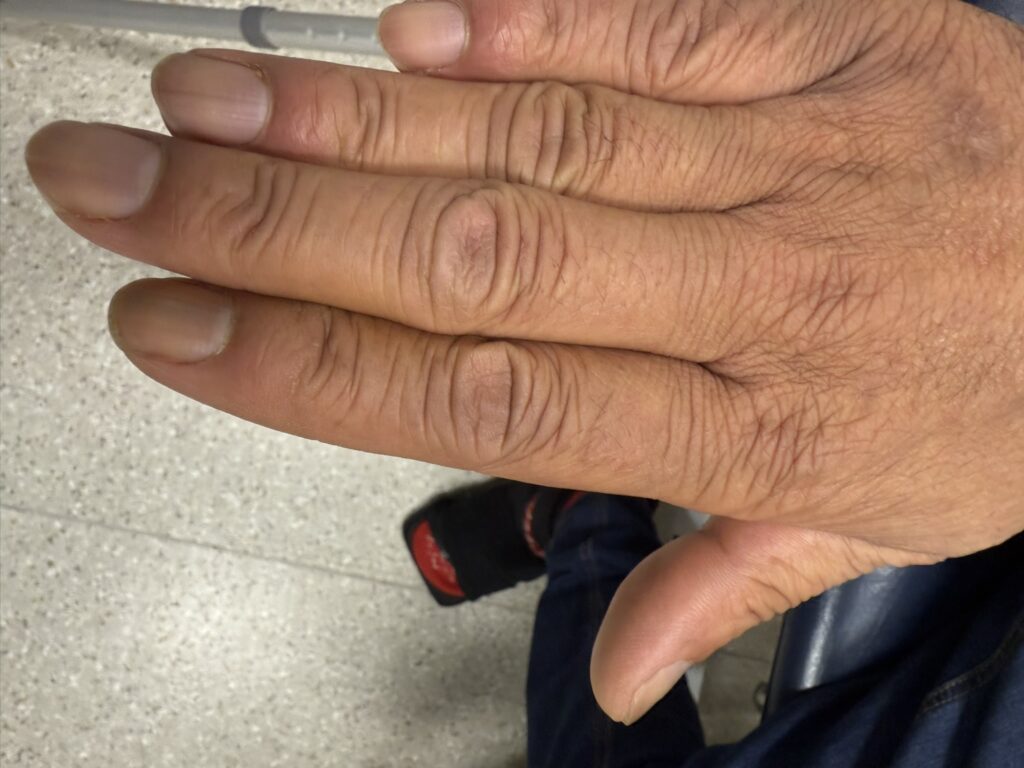
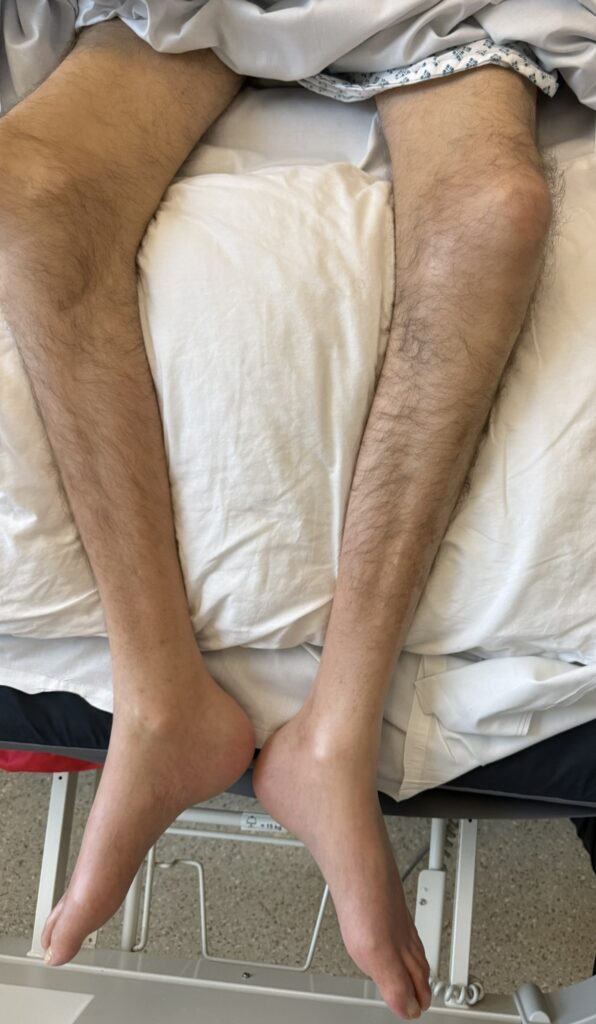
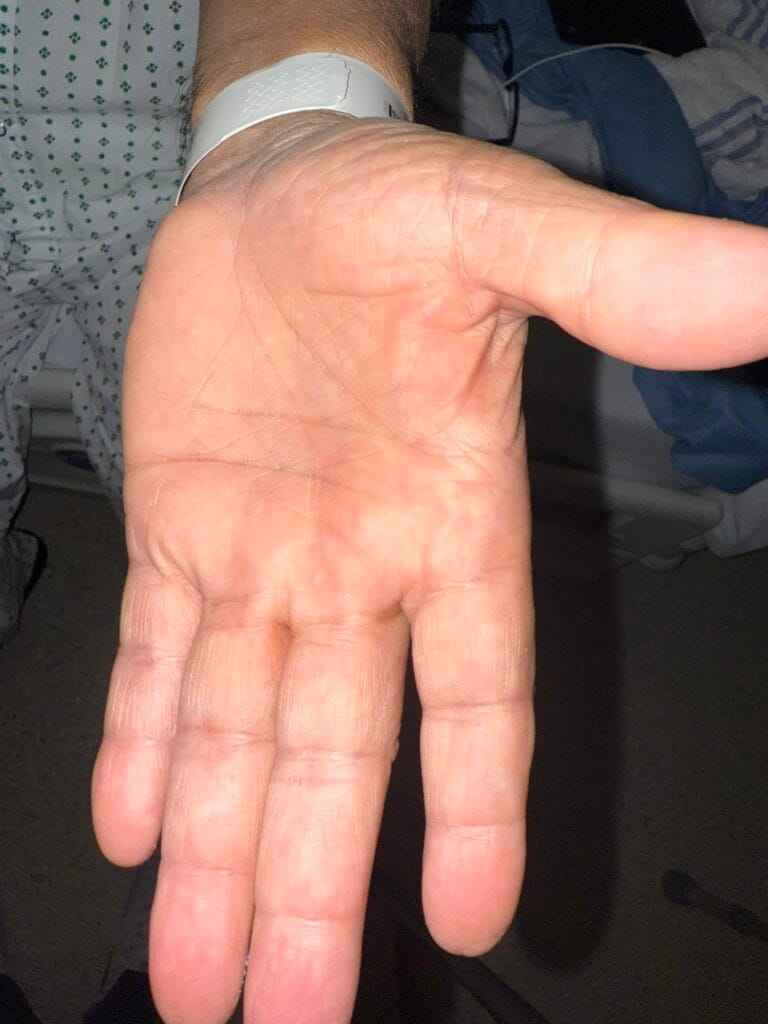
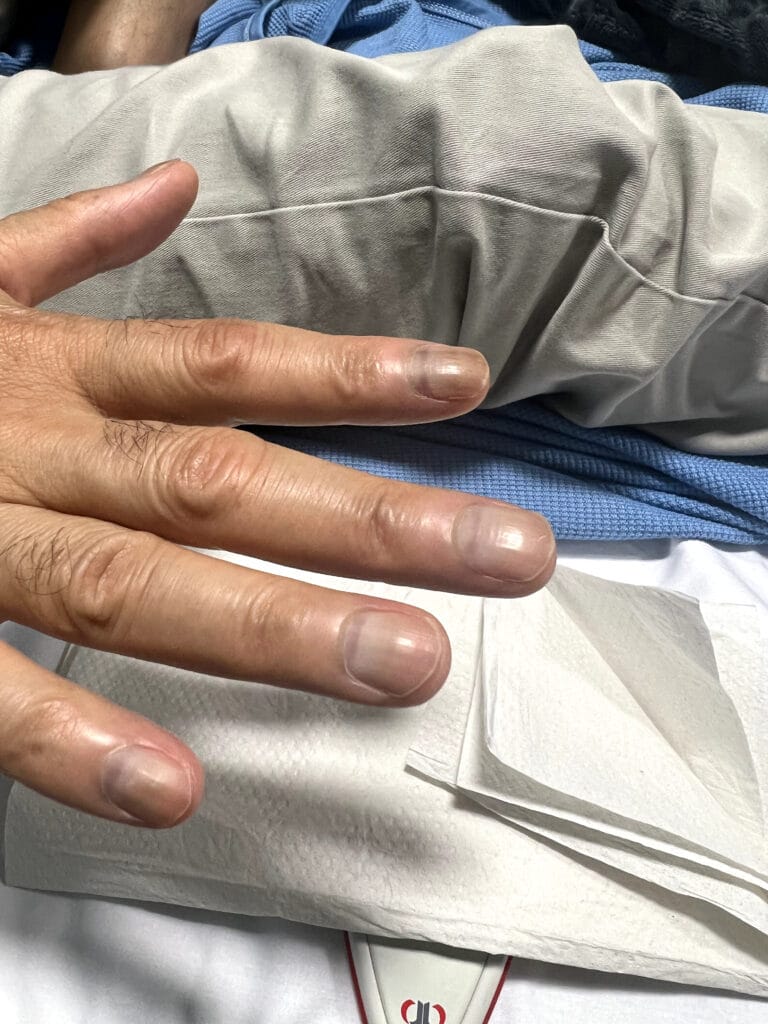
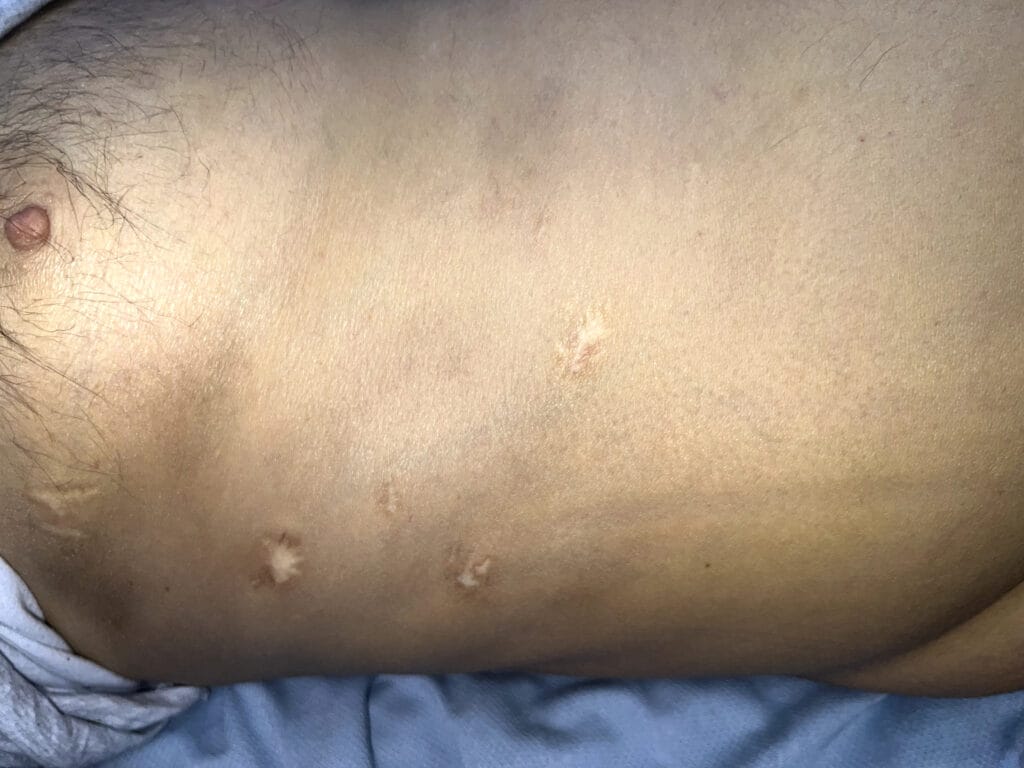
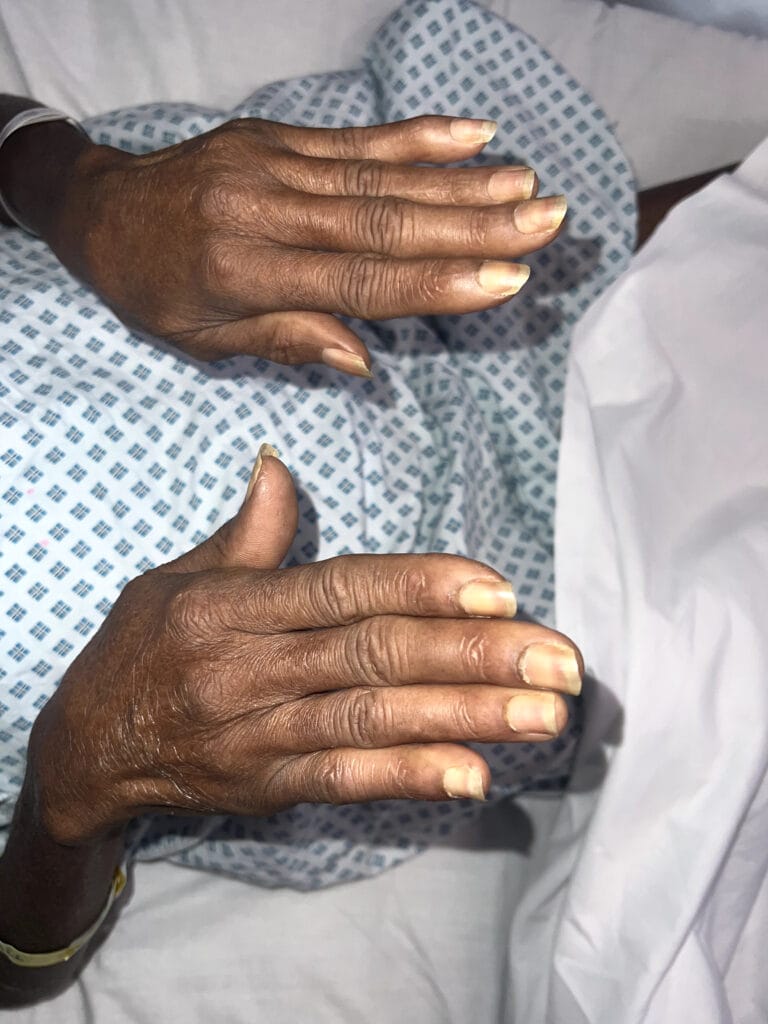
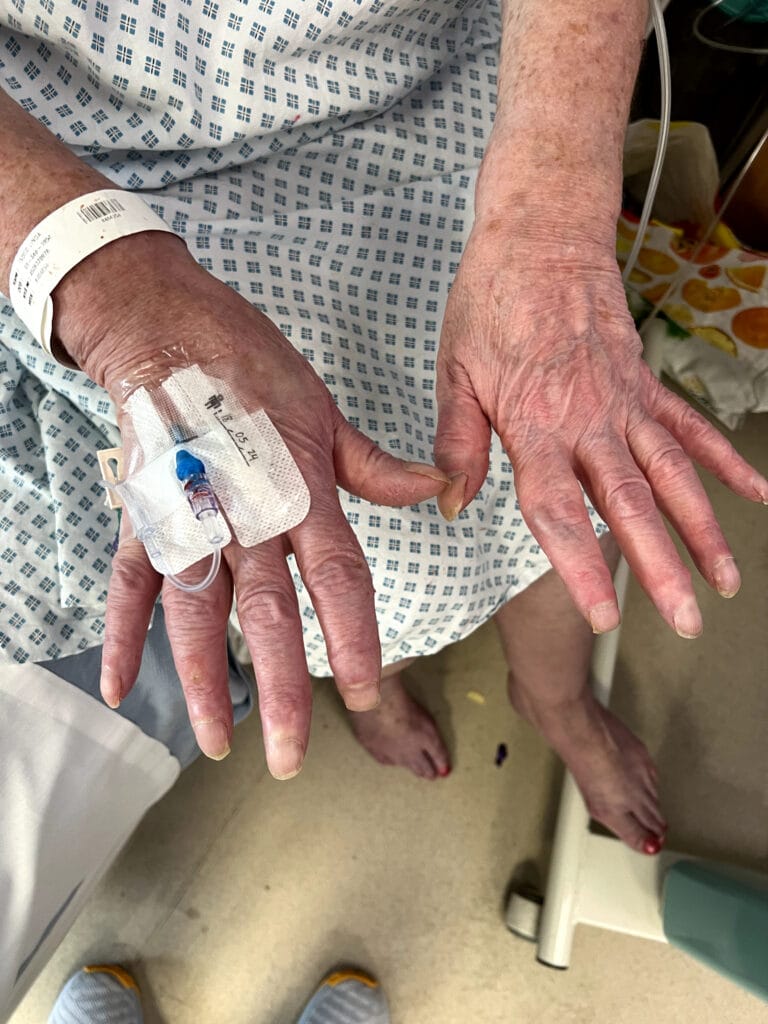
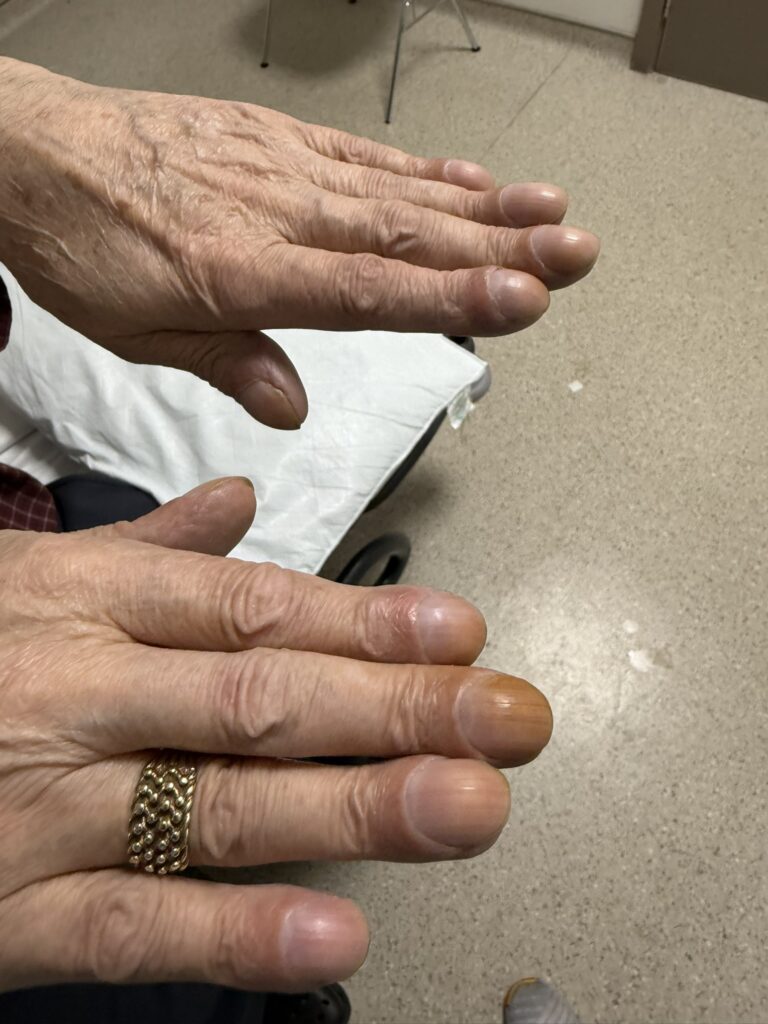
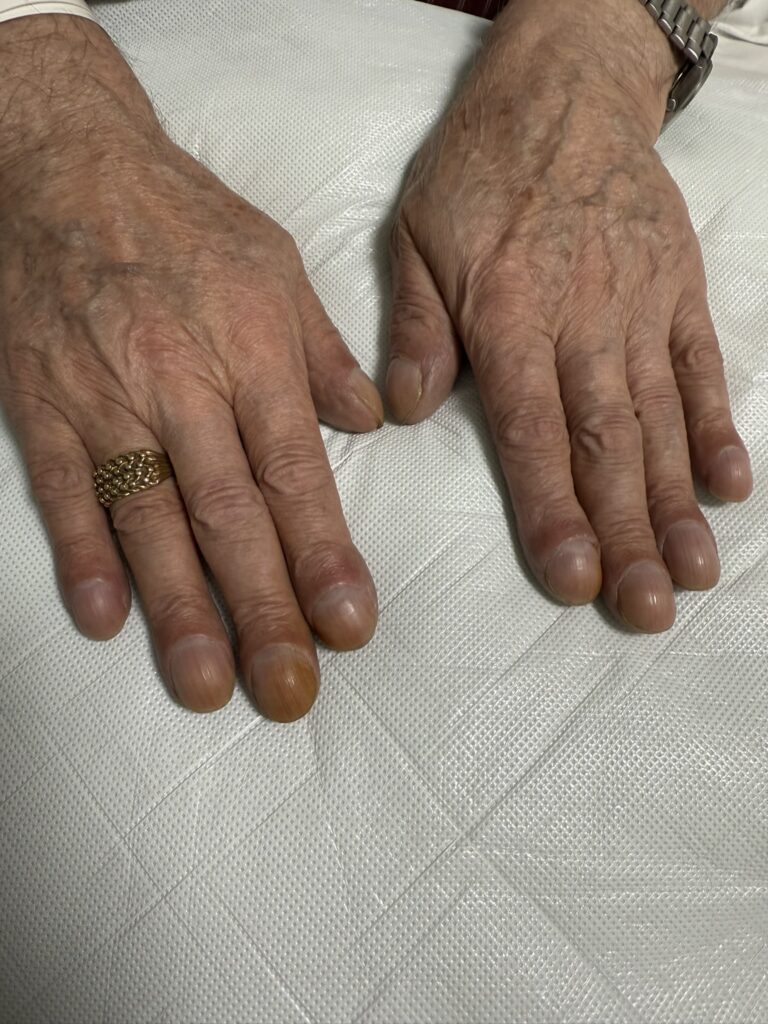
Skin changes: pretibial myxedema, nail changes or clubbing
Risk Factors & Family History
Autoimmune history: personal/family thyroid or other autoimmune disease
Lifestyle triggers: smoking, stress, infection, pregnancy or postpartum onset
Medication, Treatment & Surveillance
Prior therapy: antithyroid drugs, radioiodine, surgery
Medication side-effects: agranulocytosis, hepatic issues
Prior ophthalmology intervention: glucocorticoids, decompression, prism glasses
2. Key Examination Findings
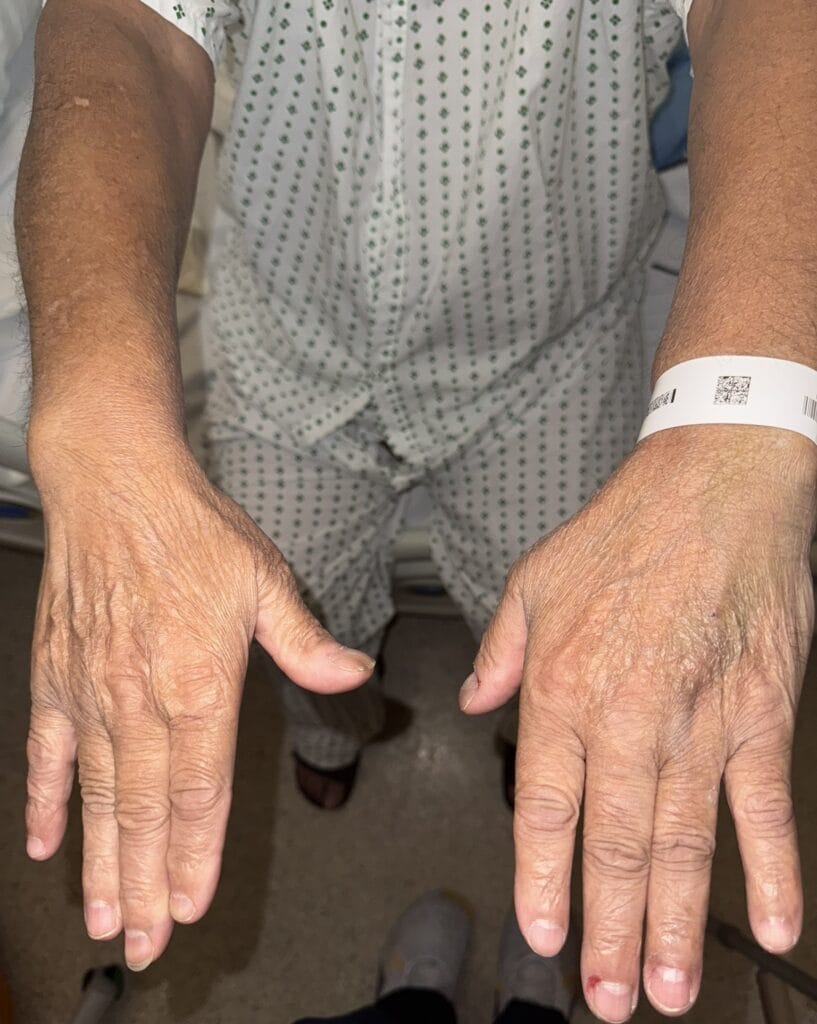
General signs: anxious, sweaty, tremor, warm skin, weight loss
Cardiac: tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, hypertension, possible heart failure
Neck: diffuse goitre ± bruit, tenderness, possible compressive symptoms
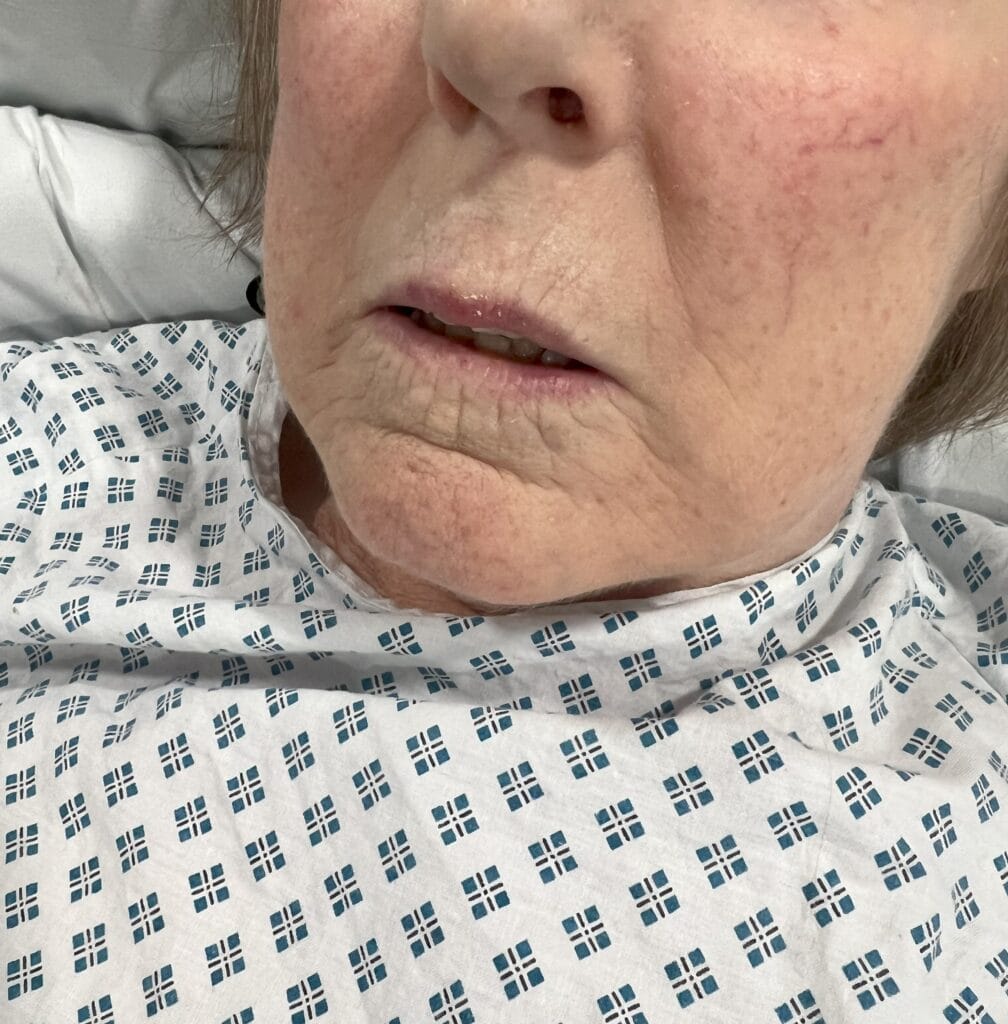
Eyes: lid lag, lid retraction, periorbital oedema, proptosis, motility restriction, conjunctival injection
Skin/extremities: pretibial myxedema, warm/moist skin, fine hair; digital clubbing in rare thyroid acropachy
3. Specific Investigations
Laboratory Work-Up:
Thyroid function tests (low TSH, elevated free T4/T3)
TSH receptor antibodies (TSI/TBII) or anti-TPO/anti-thyroglobulin as required
Imaging:
Radioactive iodine uptake scan: diffuse increased uptake typical of Graves’
Thyroid ultrasound/Doppler if suspicion of nodules, cancer, or iodine exposure contraindications
Ophthalmological assessment:
Assess for thyroid ophthalmopathy / Disease activity via Clinical Activity Score (CAS)
Cardiac & Bone:
ECG (for AF), chest X‑ray if heart failure suspected, DEXA if prolonged thyrotoxicosis
4. Management
Beta‑blockers (e.g., propranolol): symptomatic control (palpitations, tremor) while awaiting definitive therapy
Antithyroid medications: carbimazole/methimazole (first-line in UK), propylthiouracil (first trimester pregnancy) – monitor for agranulocytosis, hepatotoxicity
Radioactive iodine therapy: definitive treatment; watch for aggravation of eye disease, long-term hypothyroidism risk
Surgery (thyroidectomy): for large goitre, suspicion of cancer, or when rapid control needed; requires euthyroid state pre-op; risks include nerve injury, hypoparathyroidism
Eye disease management: mild cases with lubricants and NSAIDs; severe optic neuropathy managed with steroids or surgical decompression, smoking cessation crucial
Grave’s Disease Cheat Sheet
| Domain | Summary |
|---|---|
| Genetics / Aetiology | Autoimmune hyperthyroidism; TSH-receptor antibody mediated; family history increases risk; triggers include stress, infection, smoking, postpartum |
| Epidemiology | Most common cause of hyperthyroidism (60–80%); lifetime risk ~3% in women, 0.5% in men; common age 20–50 years |
| Pathophysiology | TSHR-autoantibodies stimulate thyroid hormone production; associated with orbitopathy and dermopathy |
| History | Weight loss, heat intolerance, tremor, palpitations, anxiety, diarrhea, amenorrhea, eye symptoms, pretibial myxedema |
| Examination | Diffuse goitre with bruit, lid lag, lid retraction, exophthalmos, periorbital edema, tachycardia/AF, warm moist skin, fine tremor |
| Differentials | • Toxic multinodular goitre • Subacute (De Quervain’s) thyroiditis • Hashimoto’s Throiditis (acute phase) • TSH-secreting pituitary adenoma |
| Investigations | TFTs (low TSH, high free T4/T3), TSH receptor antibodies (TRAb), RAI uptake scan (diffuse uptake), thyroid ultrasound, ECG, ophthalmology |
| Management | Beta-blockers for symptoms, antithyroid drugs (carbimazole/PTU), radioactive iodine therapy, surgery (thyroidectomy), smoking cessation, eye management (lubricants, steroids, decompression if severe) |